FADs: The Ocean's Fish Magnets Benefiting Fishermen
By. Tri - 26 May 2025
lautnusantara.com_ For many coastal communities, the ocean is a lifeline. One innovation that has long helped fishermen boost their catches is the Fish Aggregating Device (FAD), locally known as "rumpon" in Indonesia. This fishing aid acts like a "magnet," attracting and concentrating schools of fish, making them easier targets for primary fishing gear.
What is a FAD
Simply put, a FAD is a fishing aid deployed in marine waters, both shallow and deep. Its purpose is to create an artificial habitat that lures fish to gather around it. These concentrated fish then become much more accessible to fishermen.
A FAD itself doesn't directly catch fish; rather, it serves as a Fishing Aggregating Device (FAD). Its function is similar to an oasis in a desert, where various creatures gather to find resources or shelter.
Construction and Types of FADs
A FAD generally consists of several basic components:
- Buoy: Located on the water's surface, it keeps the FAD afloat and visible.
- Attractor: This is the core part that attracts fish. It's usually made from materials like coconut leaves, frayed ropes, old tires, or other objects that resemble marine organisms or provide shelter. These attractors are suspended from the main line.
- Main Line: Connects the buoy, attractors, and the weight at the seabed.
- Weight: Composed of rocks, concrete, or an anchor, its function is to hold the FAD in its desired position on the seabed.
Based on their deployment, FADs are categorized into two main types:
- Anchored FADs: Permanently deployed with an anchor or weight on the seabed. These typically include surface FADs (attractors in the shallow water column) and bottom FADs (attractors near the seabed).
- Drifting FADs: Do not use an anchor and are allowed to drift with ocean currents. This type of FAD offers more flexibility but is harder to control in terms of position.
There are several theories as to why fish are attracted to FADs:
- Shelter: FADs provide a structure that can offer refuge for smaller fish from predators, or for larger fish to hide from strong currents.
- Food Source: Microorganisms and algae can grow on the FAD's structure, attracting small herbivorous fish, which in turn draw in larger carnivorous fish.
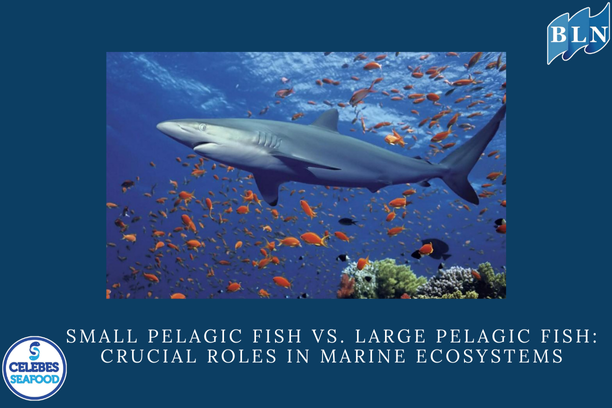
- Gathering Point: For pelagic fish (those that live in the open water column) that often migrate, FADs can serve as a reference point or a gathering place before continuing their journey.
- Spawning and Breeding: Some fish species may use FADs as a site for spawning or breeding.
Fishing Gear Used with FADs
FADs are highly effective when combined with the following fishing gear:
- Purse Seine: This is the most common combination, especially for catching large pelagic fish like tuna (skipjack, frigate tuna, yellowfin tuna). The purse seine encircles the concentrated school of fish around the FAD, maximizing the catch.
- Handline: Fishermen use handlines vertically around the FAD to catch fish such as tuna, skipjack, or Indian mackerel.
- Gillnet: While less common, some fishermen also use gillnets in the vicinity of FADs.
The most frequently found and targeted fish around FADs are pelagic species, including skipjack, frigate tuna, yellowfin tuna, mackerel scad, Indian mackerel, round scad, fringescale sardinella, and shortfin scad.
Positive and Negative Impacts of FADs
The use of FADs offers many advantages but also carries potential impacts that need careful consideration.
Positive Impacts:
- Fishing Efficiency: Fishermen don't have to spend time and fuel searching for fish schools, as the fish are already concentrated at one point.
- Increased Production: The high concentration of fish potentially boosts the volume of catches.
- Reduced Operational Costs: Saves fuel and travel time at sea.
- Gear Selectivity: With FADs, fishermen can use more selective fishing gear compared to destructive fishing methods.
Negative Impacts:
- Potential Catch of Immature Fish: If not regulated, fishing around FADs, especially with purse seines, can net young fish that haven't had a chance to reproduce.
- Overfishing: Uncontrolled use of FADs can lead to overfishing in an area, threatening the sustainability of fish resources.
- Conflict Among Fishermen: Ownership and use of FADs can trigger conflicts among fishermen.
- Ecological Impact: Changes in fish behavior or potential disruption to natural food chains if fish populations become too concentrated.
Regulation and Management
Given their potential negative impacts, many countries, including Indonesia, have implemented regulations regarding the deployment and use of FADs. The goal is to ensure the sustainability of fisheries resources and prevent conflicts of interest. Good FAD management involves determining appropriate locations, limiting their numbers, and monitoring the types and sizes of fish caught.
FADs are an example of how simple technology can provide significant benefits to fishermen. However, like any innovation, wise management is crucial to ensure that its benefits can continue to be enjoyed without sacrificing the health of the marine ecosystem.
If you are interested in our Coral Trout Fillet Skin On, CORAL TROUT WGG WHOLE GILLED GUTTED, TOMATO COD WHOLE GILLED GUTTED please do not hesitate to contact us through email and/or whatsapp.




 in Ball Shape (Balltype) for Export.jpg)
.jpg)