The Agribusiness Process in Fisheries
By. Rani - 12 Sep 2025
lautnusntara.com Indonesia is well-known as an archipelago, a fact highlighted by its many islands with vast potential for abundant and diverse fish resources. The economic value of the fisheries industry, which includes marine and freshwater biotechnology, generates significant foreign exchange for the country each year. This great economic value is currently only derived from the production and processing (post-harvest) activities of fishery products.
Fisheries business activities can create a wide-ranging economic impact on supporting industries (such as nets, boat engines, pond aerators, fish feed factories, ice factories, and cold storage), as well as on transportation services, hotels, banks, and more.
The well-managed, responsible, and sustainable development of marine and fisheries potential will support the creation of a fisheries industrialization in Indonesia. To achieve maximum results from their fisheries business, players in the fisheries agribusiness sector must master several factors: product planning, the supply chain, fisheries logistics, and the production process.
Fishery Product Planning
Product planning is the activity of formulating a product that will serve as the business's commodity. The definition of product planning is the process of deciding what and how much a company will produce within a specific period in the future.
Production planning can also be defined as a process to produce goods over a certain period, determined by organizing resources like labor, raw materials, and other equipment. Planning for a product or service involves various activities such as market testing, product and brand positioning, utilizing warranties, packaging, determining product options, product features, style, and quality, removing old products, and providing customer service.
In the fisheries agribusiness sector, product planning includes activities like planning for a specific fish seed for a production period, planning to create processed fishery products, planning for the production of tiger prawns, or planning to produce fish from grow-out operations, among others.
Planning in the fisheries business must be done with careful consideration and a high sense of responsibility. The ability to plan fishery products is one of the leadership skills that a fisheries agribusiness entrepreneur must master. This leadership ability is essential for:
-
Making decisions and managing risks
-
Deciding to become an independent entrepreneur
-
Developing a resilient attitude
-
Managing conflicts
-
Knowing the vision, mission, and planning the strategies to be implemented.
The Fishery Business Supply Chain
In principle, industrial activities, such as in manufacturing, convert raw materials and supporting materials into a finished product (ready for use) and distribute it to customers. The activity of transforming raw materials into a finished product and then delivering it to customers is called the Supply Chain.
In all business activities, including fisheries agribusiness, the supply chain must be managed effectively and efficiently to increase business profits. To get maximum results from this supply chain activity, professional management is usually required. This management is typically called Supply Chain Management (SCM).
The brief definition of Supply Chain Management (SCM) is a series of activities that include the coordination, scheduling, and control of procurement, production, inventory, and delivery of products or services to customers. This encompasses daily administration, operations, logistics, and information processing from the customer to the supplier.1
A simpler definition is that Supply Chain Management is the mechanism that connects all relevant parties and activities involved in converting raw materials into finished goods. These parties and activities are responsible for delivering the finished goods to customers at the right time and place in the most efficient way.
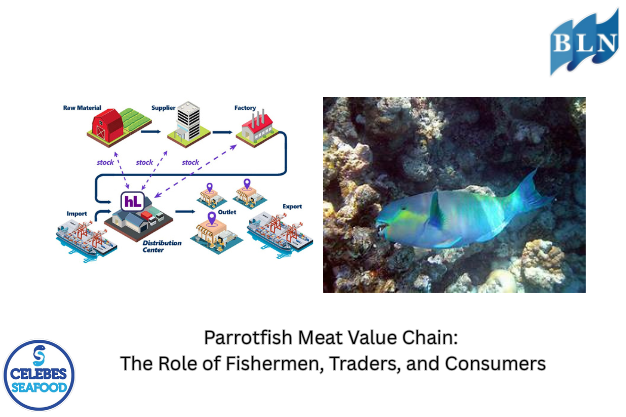
In fisheries agribusiness, the business often involves not only selling fish directly but also other products with fish as the main raw material, referred to as fishery products. A fishery product is any food product that is a whole fish or a product containing parts of a fish, including products that have been processed in any way with fish as the main ingredient. Thus, the flow or sequence of products from the producer to the consumer constitutes the supply chain. For example, here is a fisheries agribusiness supply chain:
Logistics in the Fisheries Business
Fisheries logistics activities are a continuation of supply chain management (SCM). The sequence of fisheries logistics activities starts from fishery production or products, raw materials, and production tools, and extends to the processing of information about the procurement, storage, and distribution of fishery products to consumers.
The government, through the Regulation of the Minister of Marine Affairs and Fisheries of the Republic of Indonesia Number 5/Permen-Kp/2014, defines the National Fish Logistics System, abbreviated as SLIN, as follows:
SLIN is a supply chain management system for fish and fishery products, materials and production tools, and information from procurement and storage to distribution, as a unified policy to increase capacity and stabilize the upstream-downstream fisheries production system, control price disparities, and meet domestic consumption needs.
From the definition of the National Fish Logistics System above, several logistical activities that must be mastered by business managers in fisheries agribusiness can be mapped out:
-
Mastery of the fish supply chain management system
-
Provision of fishery products
-
Provision of materials and production tools
-
The ability to gather information from procurement, storage, to distribution
-
Formulating business policies to increase the capacity and stability of the fisheries production system
-
Controlling price disparities
-
The ability to meet consumption needs
The Fisheries Business Production Process
The most important activity of a business is the product itself. A product is a good or service that can be bought and sold, which is the result of production activities. The activities to produce a product are known as production processes.
A production process is the interaction between raw materials, auxiliary materials, labor, and the machines and equipment used. According to the expert Subagyo, a production process is the process of inputs becoming outputs.
Subagyo (2000) explains that there are three types of production processes: continuous, intermittent, and intermediate. Here is an explanation of the production processes:
-
Continuous Production Process: This is a production process that never changes the type of goods being worked on.
-
Intermittent Production Process: This process is called intermittent because the production process is interrupted whenever there is a change in the type of goods being worked on.
-
Intermediate Production Process: In actual production activities, continuous and intermittent processes are not fully applied. They are usually a mixture or combination of the two. This is because the types of products are different, but their variety is not too large, and the quantity of each type is relatively high.
In fisheries agribusiness, the activities or production processes can be categorized into three types:
-
Production Process Through Aquaculture Activities: This process usually yields products such as fish seeds, fish ready to become broodstock, and fresh fish for consumption. The production activities are spawning, which produces fish larvae; nursing, which produces fish seeds; and grow-out, which produces fish ready for consumption and future broodstock.
-
Fish Catching Production Process: The production process in the fish catching sector is usually carried out in open waters, such as the sea. Marine fisheries have a great variety of species, especially if humans are able to analyze the fish on the seabed. However, current human capabilities and equipment are still very limited. Fish catching at sea is an activity carried out all over the world, except in areas where the water depth is unreachable, currents are too strong and dangerous, and in waters that are restricted by international law. The products resulting from the fish catching process are fresh marine fish, shellfish, and seaweed.
-
Processing Production Process of Fishery Products: The production process in the processing of fishery products is very diverse. It includes making canned food with fish as the main ingredient, smoked fish products, fermented fish, salted fish, and others. The handling of processed fish products has its own level of complexity, from providing high-quality fish raw materials to ensuring a clean (hygienic) production process and more aggressive marketing. Business players in fish processing play an important role in supplying nutrients to consumers. Consumers who do not like whole fish can get nutrients from it, like protein and essential amino acids, through processed products made from the fish itself.
If you are interested in our Red Emperor Fillet Skin On, Red Snapper Fillet Skin On please do not hesitate to contact us through email and/or whatsapp.